Foreword
machine learning algorithms pre-requisite knowledge:
- Programming languages and data analysis tools
- Large-scale computation and the associated frameworks
- Mathematics and statistics and how machine learning builds on it
Table of Symbols
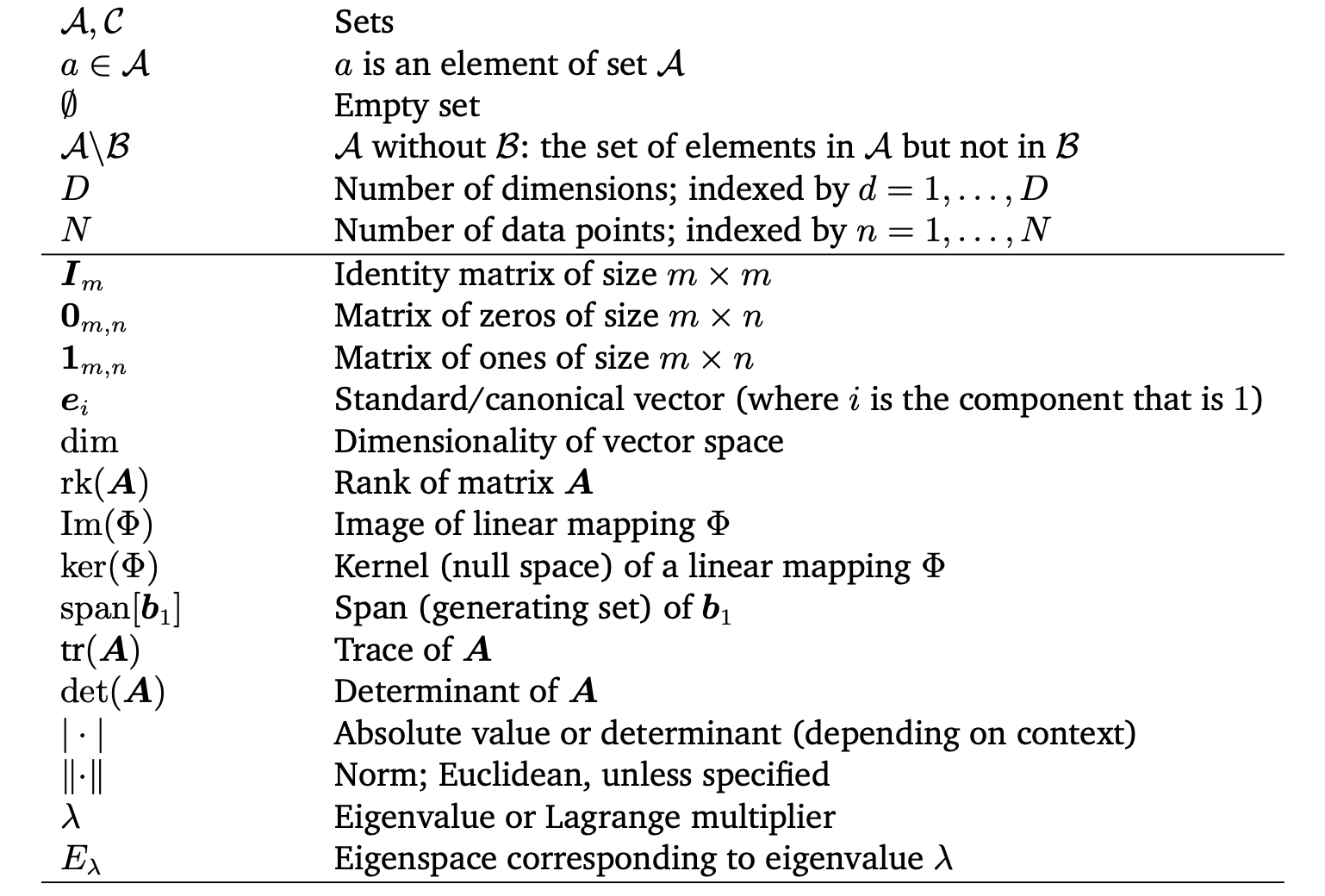
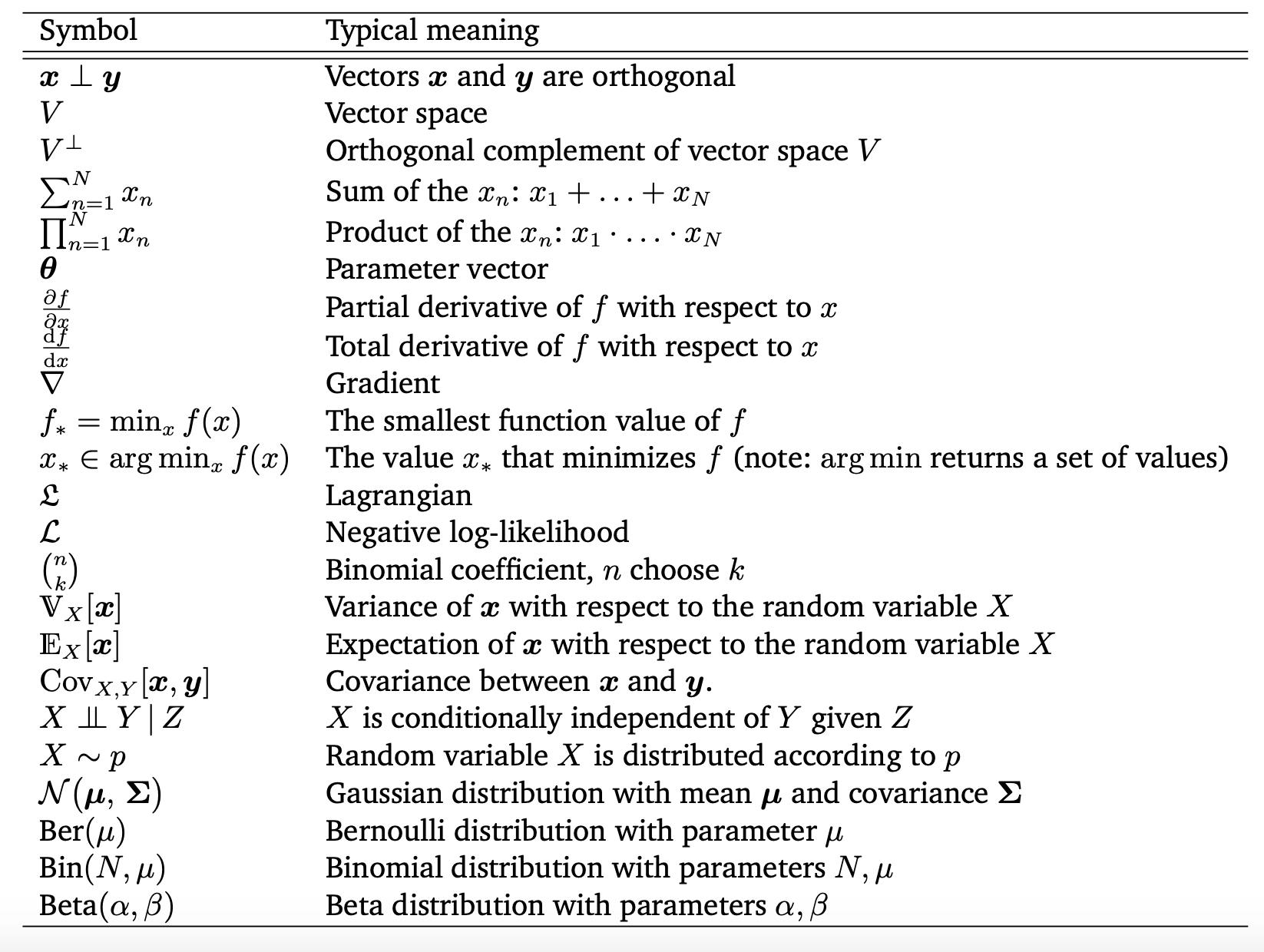
Table of Abbreviations and Acronyms
| Acronym | Meaning |
|---|---|
| e.g. | Exempli gratia (Latin: for example) |
| GMM | Gaussian mixture model |
| i.e. | Id est (Latin: this means) |
| i.i.d. | Independent, identically distributed |
| MAP | Maximum a posteriori |
| MLE | Maximum likelihood estimation/estimator |
| ONB | Orthonormal basis |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PPCA | Probabilistic principal component analysis |
| REF | Row-echelon form |
| SPD | Symmetric, positive definite |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
Linear Algebra
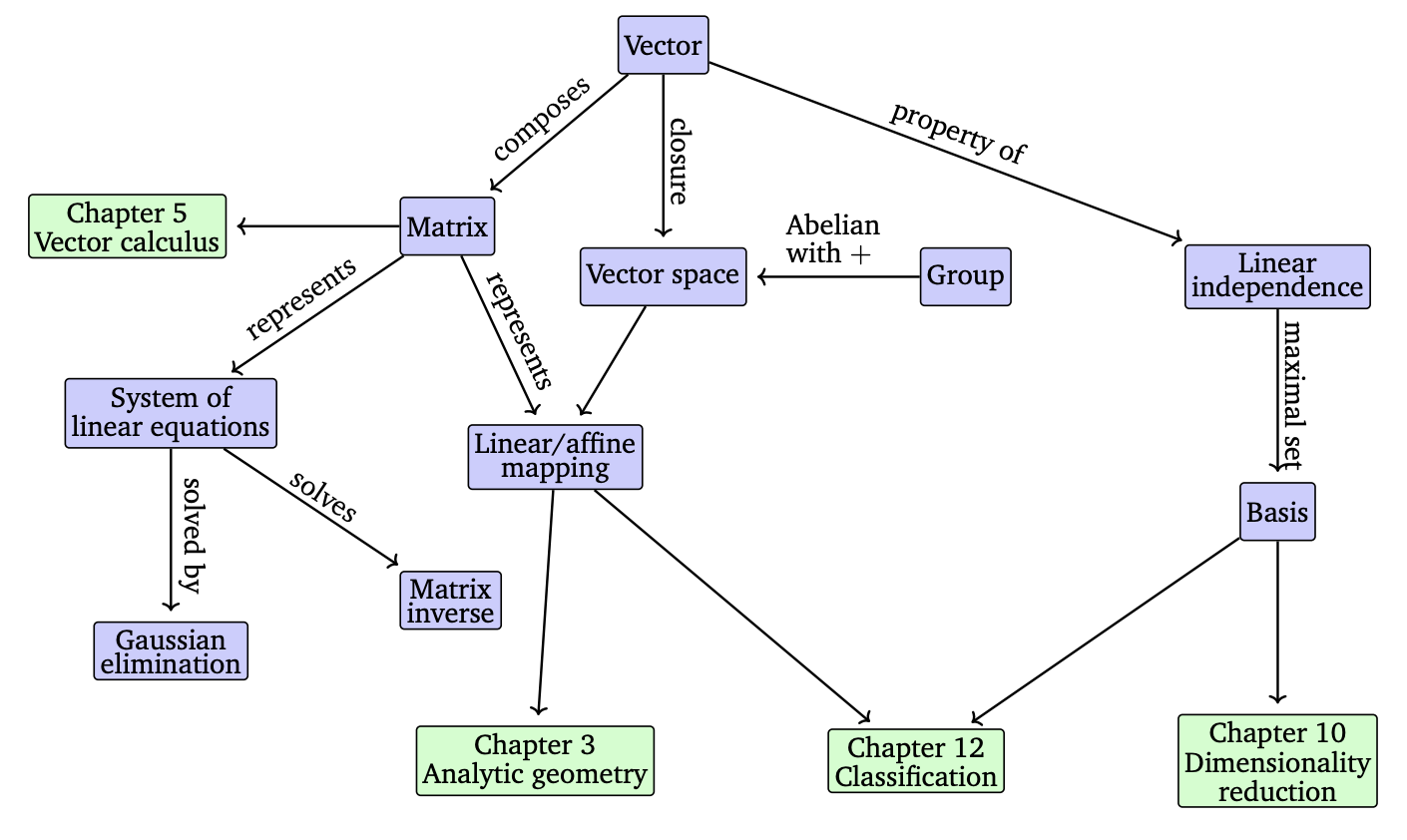
Figure 2.2 A mind map of the concepts introduced in this chapter, along with where they are used in other parts of the book.
Other excellent resources are Gilbert Strang’s Linear Algebra course at MIT and the Linear Algebra Series by 3Blue1Brown.
Page 19.
